Gemological Education
The rarest and most expensive are diamonds in the colourless range graded D,E and F on a scale that descends to Z. Diamonds with more colour than Z, or in other shades such as orange, pink, blue, etc. are classified as "Fancy Colored Diamonds" and are graded on the
HGL Color Diamond Report

To determine the correct color, all submitted diamonds are compared to an internationally accepted master set of stones, the colors of which range from D, or colorless (the most sought after) to Z, the most yellow/brown - aside from "fancy" yellow or brown.
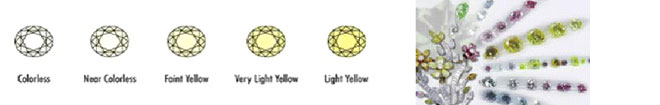
HGL assigns a color grade fordiamonds in the D-Z range with the diamond face-down and viewed through the pavilion. This is because size, shape, cut quality and the presence of fluorescence can influence visible face-up color. In fact, lighting, mounting choice and even the clothes one wears have an impact on color, so IGI uses the most neutral environment possible to ensure accurate and consistent results.
 Since diamonds form under extreme heat and pressure, internal and external characteristics are common. These characteristics help gemmologists separate natural diamonds from synthetics and identify individual stones.
Since diamonds form under extreme heat and pressure, internal and external characteristics are common. These characteristics help gemmologists separate natural diamonds from synthetics and identify individual stones.There are two types of clarity characteristics: inclusions and blemishes. In order to grade the clarity of a diamond, it is necessary to observe the number and nature of external and internal characteristics of the stone, as well as their size and position.
The difference is based on their locations: inclusions are enclosed within a diamond, while blemishes are external characteristics.
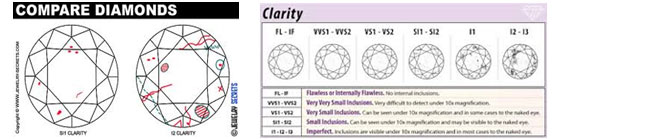
HGL grading reports show plotted diagrams of clarity characteristics marked in red for internal, and green for external features; they are useful for identification.

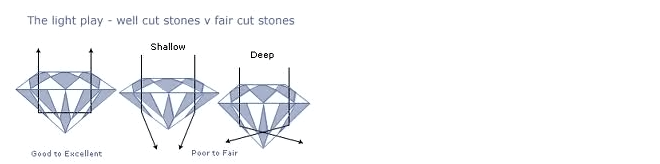
While nature determined the color and clarity of a natural diamond, man is responsible for the cut quality which brings it to life.
You can also open a tab or a bookmark from a link anywhere on the page. The planning, proportions, cutting precision and details of finish determine how brilliant, dispersive and scintillating the diamond will be. If the cutting factors under man's control are not optimized, the appearance of the diamond can be adversely affected.
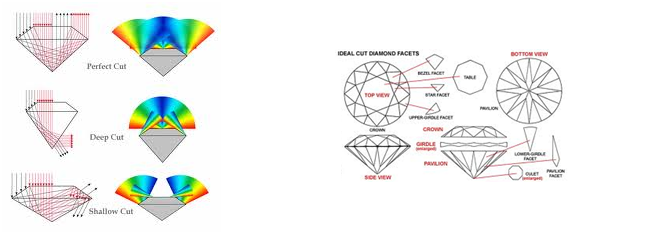
Diamond faceting has changed over time, particularly as lighting has evolved. There are many shapes and cutting styles, each with different visual properties. The most popular diamond in the age of modern electric lighting is the Round Brilliant.
When a ray of light touches the surface, part of it is reflected back. This is external refraction.
- 1. The rest of the ray penetrates the stone and moves through it. This is known as refraction
- 2. The part of the ray reflected back to the surface exits, broken into spectral colors in a prism-like effect. This is known as dispersion.
Elements of diamond beauty can be described as brilliance (all light returning to the eye), dispersion or 'fire' (seen as white light is broken into spectral colors), contrast patterns (contrasting light and dark areas created by the viewer's reflection) and scintillation or 'sparkle' (seen as the diamond, the light source or the observer move). These qualities combine to create the life of the diamond and the way it reacts to lighting and environment.

The weight or size of a diamond is measured in carats (ct.).
One carat weighs 1/5 of a gram and is divided into 100 points, so a diamond weighing 1.07carat is referred to as "one carat and seven points."
For Example
0.75 carat = 75 points.
1/2 carat = 50 points.
1/4 carat = 25 points.
With an accuracy of 1/100,000 carat, the IGI scales provide a highly precise diamond weight, down to the hundredth or thousandth of a carat.
It is important to note that diamonds of the same weight don't necessarily have the same size appearance. Those cut too shallow or deep may look small for their weight, or suffer in brilliance. As a reference, IGI recommends the following vertical spreads for round brilliant diamonds.
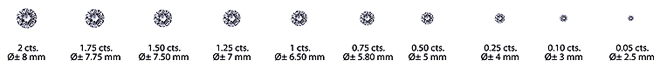
When diamonds are mined, large gems are discovered much less frequently than small ones, which make large diamonds much more valuable.
Diamond prices rise exponentially with carat weight. So, a 2-carat diamond of a given quality is always worth more than two 1-carat diamonds of the same quality.
